...
| 코드 블럭 |
|---|
| language | bash |
|---|
| theme | DJango |
|---|
| title | npm을 이용한 aws-cdk 설치 명령 |
|---|
|
npm install -g aws-cdk |
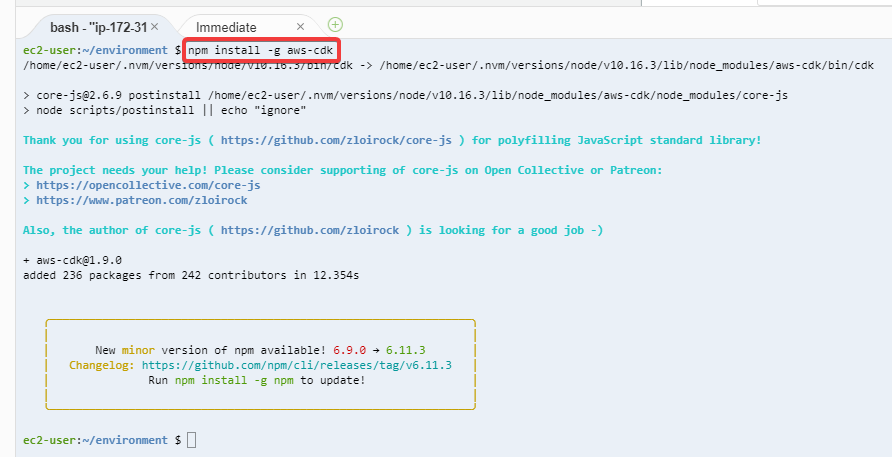
npm 업데이트가 있을 경우 npm도 업데이트 합니다.
| 코드 블럭 |
|---|
| language | bash |
|---|
| theme | DJango |
|---|
| title | npm 업데이트 |
|---|
|
npm install -g npm |
 Image Removed
Image Removed
프로젝트 시작
프로젝트 생성
프로젝트 디렉토리를 생성하고 이동합니다.
...
| 코드 블럭 |
|---|
| language | bash |
|---|
| theme | DJango |
|---|
| title | url_shortener_stack.py에서 CDK를 이용한 DynamoDB Table 생성 코드 |
|---|
|
table = aws_dynamodb.Table(self, "mapping-table",
partition_key = aws_dynamodb.Attribute(name="id",type=aws_dynamodb.AttributeType.STRING)) |
...
| 코드 블럭 |
|---|
| language | py |
|---|
| theme | RDark |
|---|
| title | lambda에서 사용할 handler.py 코드 |
|---|
| linenumbers | true |
|---|
|
import json
import os
import uuid
import logging
import boto3
LOG = logging.getLogger()
LOG.setLevel(logging.INFO)
def main(event, context):
LOG.info("EVENT: " + json.dumps(event))
query_string_params = event["queryStringParameters"]
if query_string_params is not None:
target_url = query_string_params['targetUrl']
if target_url is not None:
return create_short_url(event)
path_parameters = event['pathParameters']
if path_parameters is not None:
if path_parameters['proxy'] is not None:
return read_short_url(event)
return {
'statusCode': 200,
'body': 'usage: ?targetUrl=URL'
}
def create_short_url(event):
# Pull out the DynamoDB table name from environment
table_name = os.environ.get('TABLE_NAME')
# Parse targetUrl
target_url = event["queryStringParameters"]['targetUrl']
# Create a unique id (take first 8 chars)
id = str(uuid.uuid4())[0:8]
# Create item in DynamoDB
dynamodb = boto3.resource('dynamodb')
table = dynamodb.Table(table_name)
table.put_item(Item={
'id': id,
'target_url': target_url
})
# Create the redirect URL
url = "https://" \
+ event["requestContext"]["domainName"] \
+ event["requestContext"]["path"] \
+ id
return {
'statusCode': 200,
'headers': {'Content-Type': 'text/plain'},
'body': "Created URL: %s" % url
}
def read_short_url(event):
# Parse redirect ID from path
id = event['pathParameters']['proxy']
# Pull out the DynamoDB table name from the environment
table_name = os.environ.get('TABLE_NAME')
# Load redirect target from DynamoDB
ddb = boto3.resource('dynamodb')
table = ddb.Table(table_name)
response = table.get_item(Key={'id': id})
LOG.debug("RESPONSE: " + json.dumps(response))
item = response.get('Item', None)
if item is None:
return {
'statusCode': 400,
'headers': {'Content-Type': 'text/plain'},
'body': 'No redirect found for ' + id
}
# Respond with a redirect
return {
'statusCode': 301,
'headers': {
'Location': item.get('target_url')
}
} |
...

IAM 설정이 변경된 것을 볼 수 있으며, DDB mapping-table에 mapping에 대한 Lambda 함수에 정책이 추가된 것을 볼 수 있습니다. backend라는 Lambda 함수가 이 정책을 쓰는 주체가 되는 것을 알 수 있습니다.
Lambda 함수가 수정된 것을 볼 수 있으며, 환경 변수 값이 추가되었고 새롭게 만들어진 정책이 적용된 것을 볼 수 있습니다.
...
| 코드 블럭 |
|---|
| language | py |
|---|
| theme | RDark |
|---|
| title | url_shrotener_stack.py |
|---|
| linenumbers | true |
|---|
|
import os
from aws_cdk import core, aws_dynamodb, aws_lambda, aws_apigateway, aws_ecs, aws_ec2
from traffic import Traffic
import os
# we need default values here since aws-cdk-examples build synthesizes the app
ACCOUNT= os.environ['CDK_DEFAULT_ACCOUNT']
REGION = os.environ['CDK_DEFAULT_REGION']
VPC_ID = os.environ.get('TESTENV_VPC_ID', 'vpc-0e680e107cb16f0c90e3593e52a4149549')
AWS_ENV = core.Environment(account=ACCOUNT, region=REGION)
class UrlShortStack(core.Stack):
def __init__(self, scope: core.Construct, id: str, **kwargs) -> None:
super().__init__(scope, id, env=AWS_ENV, **kwargs)
# The code that defines your stack goes here
table = aws_dynamodb.Table(self, "mapping-table",
partition_key = aws_dynamodb.Attribute(name="id",type=aws_dynamodb.AttributeType.STRING))
function = aws_lambda.Function(self, "backend",
runtime=aws_lambda.Runtime.PYTHON_3_7,
handler="handler.main",
code=aws_lambda.Code.asset("./lambda"))
table.grant_read_write_data(function)
function.add_environment("TABLE_NAME", table.table_name)
api = aws_apigateway.LambdaRestApi(self, "api", handler=function)
class TrafficStack(core.Stack):
def __init__(self, scope: core.Construct, id: str, **kwargs) -> None:
super().__init__(scope, id, env=AWS_ENV, **kwargs)
# lookup our pre-created VPC by ID
vpc_env = aws_ec2.Vpc.from_lookup(self, "vpc",
vpc_id=VPC_ID)
# lookup our pre-created VPC by ID
test_url = 'https://cdk.awsdemokr.com/715a930b'
Traffic(self, 'TestTraffic',
Traffic(self, 'TestTraffic', vpc= vpc_env, url=test_url, tps=10)
url="https://7vzqf6htub.execute-api.ap-southeast-1.amazonaws.com/prod/2a3c26e0",
tps=10) |
* VPC_ID는 Private subnet을 포함하고 있어야 합니다. 만약 없다면, VPC Wizard를 통해서 생성하고 해당 VPC를 연결합니다.
...
| 코드 블럭 |
|---|
| language | py |
|---|
| theme | RDark |
|---|
| title | url_shrotener_stack.py for cdk-watchful |
|---|
| linenumbers | true |
|---|
|
import os
from aws_cdk import core, aws_dynamodb, aws_lambda, aws_apigateway, aws_ecs, aws_ec2
from traffic import Traffic
import os
from cdk_watchful import Watchful
# we need default values here since aws-cdk-examples build synthesizes the app
ACCOUNT= os.environ['CDK_DEFAULT_ACCOUNT']
REGION = os.environ['CDK_DEFAULT_REGION']
VPC_ID = os.environ.get('TESTENV_VPC_ID', 'vpc-0e680e107cb16f0c90e3593e52a4149549')
AWS_ENV = core.Environment(account=ACCOUNT, region=REGION)
class UrlShortStack(core.Stack):
def __init__(self, scope: core.Construct, id: str, **kwargs) -> None:
super().__init__(scope, id, env=AWS_ENV, **kwargs)
# The code that defines your stack goes here
table = aws_dynamodb.Table(self, "mapping-table",
partition_key = aws_dynamodb.Attribute(name="id",type=aws_dynamodb.AttributeType.STRING))
function = aws_lambda.Function(self, "backend",
runtime=aws_lambda.Runtime.PYTHON_3_7,
handler="handler.main",
code=aws_lambda.Code.asset("./lambda"))
table.grant_read_write_data(function)
function.add_environment("TABLE_NAME", table.table_name)
api = aws_apigateway.LambdaRestApi(self, "api", handler=function)
wf = Watchful(self, 'monitoring', alarm_email='scv@studydev.com')
wf.watch_scope(self)
class
class TrafficStack(core.Stack):
def __init__(self, scope: core.Construct, id: str, **kwargs) -> None:
super().__init__(scope, id, env=AWS_ENV, **kwargs)
# lookup our pre-created VPC by ID
vpc_env = aws_ec2.Vpc.from_lookup(self, "vpc",
vpc_id=VPC_ID)
# lookup our pre-created VPC by ID
test_url = 'https://cdk.awsdemokr.com/715a930b'
Traffic(self, 'TestTraffic',
vpc= vpc_env,
url="https://7vzqf6htub.execute-api.ap-southeast-1.amazonaws.com/prod/2a3c26e0",
Traffic(self, 'TestTraffic', vpc= vpc_env, url=test_url, tps=10)
|
cdk-watchful 배포
| 코드 블럭 |
|---|
| language | bash |
|---|
| theme | DJango |
|---|
| title | 모든 cdk 스택 배포 |
|---|
|
cdk deploy "*" |
...
2. CDK 배포를 위해서 생성된 S3 버킷을 찾아서 파일들을 모두 삭제합니다. (cdktoolkit-stagingbucket- 접두사로 보통 시작합니다.) 그리고 Cloudformation에 생성된 CDKToolKit 스택을 삭제합니다.
| 코드 블럭 |
|---|
aws cloudformation describe-stacks --stack-name CDKToolkit --query "Stacks[0].Outputs[0].OutputValue"
aws s3 rm s3://cdktoolkit-stagingbucket-yrlacd8hy29p --recursive
|
3. 테스트를 위해 생성한 VPC에서 Nat Gateway를 삭제하고, Elastic IP를 반납한 후, CDK-TEST VPC를 삭제합니다.
...


